CLOUD BASED BUS PASS USING BARCODE SCANNER
ABSTRACT:
The Cloud based Bus Pass System Project is a real time
project which is useful for the commuters who are facing problems with the
current manual work of bus pass system. It makes the passenger easy to travel
with the ticket QR code with the mobile. So that even if the passenger loses
the ticket at the time of checking he can show the QR code. The conductor can
check the QR code with the Admin weather matches or not. The unique number
allotted for one person cannot be the same for the other. It also increases the
validity period, frequently warns to the commuters before completion of his/her
validity period by sending SMS or mails. His/her Renewal or Registration can be
done using a credit card/debit card/online/by cash. Initially, commuters need
to register with the application by submitting details like photo, address
proof and other details and submit it online. They will verify your details and
if they are valid they will approve bus pass else they will reject. You can
even renew using credit card or otherwise transaction methods. Customer can buy
the bus ticket over the Internet, 24 hours a day throughout the week, this
solves the issue of bus ticket being misplaced or stolen. The site may get overloaded due to huge
number of users visiting at once. Thus this system is built up using cloud
infrastructure for improved performance.
SCOPE:
This project is created to provide “safe, reliable,
saving, efficient and affordable” services for user. This idea would help the
user in a better way. As per the previous system the user had to do each and
every process manually, but this system helps user to make the work bit faster.
The user can then take print out of this bus pass from their mail id and use
them or even by showing the QR code in their android device they can able to
access the pass. The bus pass will be differ for different types of users. In
this bus pass, all the required details such as candidate name, address, date
of birth, mail id, name of the school(government/private), validity period,
amount paid (free for government school students) and photo copy of the
candidate are provided. Instead of school details, working organization details
will be provided in employees bus pass. The renewal process can be done either
monthly or yearly as per user wish. Based on that renewal period amount will be
deducted.
MODULES
INVOLVED:
ü Registration
Module
ü Authentication
Module
ü Online
Payment Module
ü Generation
of Bus Pass Module
ü Bus Pass
Renewal Module
ü Notification
Module
ELEMENTS:
ü Abstraction
ü Encapsulation
ü Modularity
ü Hierarchy
1. ABSTRACTION:
·
Abstraction
is the process of taking away or removing characteristics from something in
order to reduce it to a set of essential characteristics.
·
In
object-oriented programming, abstraction is one of three central principles
along with encapsulation and inheritance.
·
Through
the process of abstraction, a programmer hides all but the relevant data about
an object in order to reduce complexity and increase efficiency.
·
In the
same way that abstraction sometimes works in art, the object that remains is a
representation of the original, with unwanted detail omitted.
·
The
resulting object itself can be referred to as an abstraction, meaning a named entity made up of selected
attributes and behaviour specific to a particular usage of the originating
entity.
·
Abstraction
is related to both encapsulation and data hiding.
·
In the
process of abstraction, the programmer tries to ensure that the entity is
named in a manner that will make sense and that it will have all the relevant
aspects included and none of the extraneous ones.
·
A
real-world analogy of abstraction might work like this: You (the object) are
arranging to meet a blind date and are deciding what to tell them so that they
can recognize you in the restaurant.
·
You
decide to include the information about where you will be located, your height,
hair colour, and the colour of your jacket.
·
However,
since entities may have any number of abstractions, you may get to use them in
another procedure in the future.
·
Bus pass verification
using bar code scanner will make the work of the conductors and passengers
easy.
·
The main principle of
the system was conductor will scan the bus pass QR code of the customer that
will check for the database in cloud, if the entity exists then it will be
verified.
·
The system is not so
complex, so conductor can easily use the system to make their job done.
·
The cloud database will
be hidden for both conductors and the passengers.
·
Only the database admin
can access the database for adding/modifying the users in the database.
2. HIERARCHY:
·
The above example shows
the hierarchy of a college management system to classify students and
employees.
·
A class hierarchy or inheritance tree in computer
science is a classification of object types, denoting objects as the
instantiations of classes inter-relating the various classes by
relationships such as "inherits", "extends", "is an
abstraction of", "an interface definition".
·
In object-oriented
programming, a class is a template that defines the state and behaviour common
to objects of a certain kind.
·
A
class can be defined in terms of other classes.
·
Admin will be in the
top of the hierarchy and passengers will be at the last in bus pass using bar
code scanner system.
3. Encapsulation:
·
Encapsulation
is one of the loosely defined OOAD concepts.
·
The
term is known in software development for many years but I can't find any
reliable origin.
·
Encapsulation
is very close or similar to the abstraction concept.
·
The
difference is probably in "direction" - encapsulation is more about
hiding (encapsulating) implementation details while abstraction is about
finding and exposing public interfaces. The two concepts are supported by
access control.
·
The admin alone has
access to the database hence all the other users are encapsulated from the
system.
4. Modularity:
·
Modularity is the process of decomposing a problem (program) into a set
of modules so as to reduce the overall complexity of the problem.
·
Modularity is the property of a system that has been decomposed into a
set of cohesive and loosely coupled modules.
·
Modularity is intrinsically linked with encapsulation.
·
Modularity can be visualized as a way of mapping encapsulated
abstractions into real, physical modules having high cohesion within the
modules and their inter–module interaction or coupling is low.
·
In bus pass using bar
code scanner project, modules are separated as conductor, passenger and admin.
REUSABILITY:
ü Class
hierarchy
ü Derived
classes inherits properties and behavior of base class
ü Allows code
re-use
ü Derived
classes can have
·
additional properties and behavior
·
over-ride inherited behavior
o Reusability
is also very similar to modularity.
o Objects
are created and used several times to avoid redundancy.
Renew bus pass can be
used by students, citizens and senior citizens without making new objects.
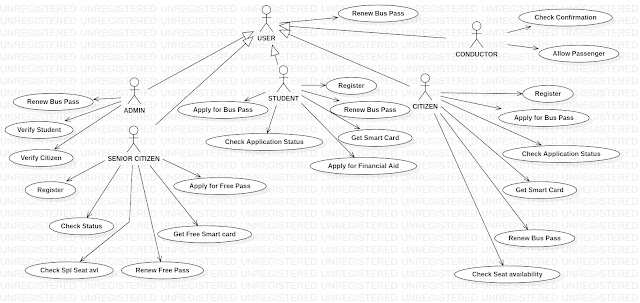
List of
actors involved:
1.
PRIMARY
ACTOR: User
2.
SECONDARY
ACTOR: Admin, Citizen, Senior Citizen, Student, Conductor
Relationship:
The primary
actor (USER) is divided into four secondary classes such as admin, citizen,
senior citizen, student and conductor.
Each secondary classes has many use cases. The detailed use case diagram of the project
is elaborately given below as a use case diagram.
Here we have used generalization, dependency,
association, direct association, etc… to explain the relationship between the
use cases.
Registration Module:
In the
registration module, the commuters are first allowed to sign in by providing
valid email id. Then they are allowed to
create their passcode. After that, by
providing valid user id and passcode they are allowed to access their portal.
Authentication Module:
In this module the registered user
details and documents are verified by the admin. Only the registered
users are allowed for renewal of their bus pass. This module checks whether the
authenticated user is accessing.
Online
Payment Module:
In this
module the registered users are allowed to pay the charges for their bus pass
renewal or applying new bus pass. The commuters will be redirected to a Payment
Gateway Process page.
Generation of Bus Pass Module:
After paying
the applicable charges the commuters can able to generate their Bus Pass in the
form of QR code. By using this QR code
they can able to travel in the allotted busses.
Bus Pass Renewal Module:
Only the
registered users are allowed to access this Bus Pass Renewal Module. In this module, the commuters can able to
renew their bus pass after the completion of the previous bus pass.
Notification Module:
In this
module, the registered users can able to receive notification in their apps and
even via emails the notification will sent.
Using this module the commuters can able to know the status of the bus
which they are going to travel.
PURPOSE
OF USE CASE DIAGRAM:
The main purpose of a use case
diagram is to show who interacts with your system, and the main goals
they achieve with it. Create Actors to represent classes of people,
organizations, other systems, software or devices that interact with your
system or subsystem.
A
use case diagram does not show the detail of the use cases: it only summarizes
some of the relationships between use cases, actors, and systems. In
particular, the diagram does not show the order in which steps are performed to
achieve the goals of each use case. You can describe those details in other
diagrams and documents, which you can link to each use case.
ADVANTAGES OF USE CASE DIAGRAM:
- Use case help to capture the functional requirements of a system.
- Use cases are traceable.
- Use cases can serve as the basis for the estimating, scheduling, and validating effort.
·
Use cases can serve as the basis for the estimating,
scheduling, and validating effort.
·
Use case can
evolve at each iteration from a method of capturing requirements, to
development guidelines to programmers, to a test case and finally into user
documentation.
·
Use case alternative paths capture additional behavior
that can improve system robustness.
·
Use cases have proved to be easily understandable by
business users, and so have proven an excellent bridge between software
developers and end users.


Comments
Post a Comment